Sortase A (Staphylococcus aureus)
Protein ↔ protein ligase (transpeptidase) and protease. Enables posttranslational protein ligation and immobilization to coated surfaces under physiological (nondenaturing) conditions.
Detailed Product Description
English Version
Deutsche Version
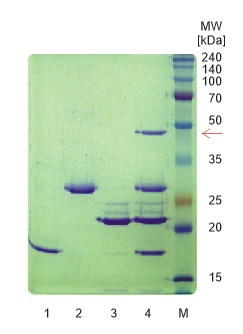
Figure 1: Sortase A mediated protein ligation. SDS PAGE gel.
Lane 1: rnpA protein with C-terminal partial sortase A recognition sequence LPET (= substrate protein),
Lane 2: GFP with N-terminal GGG (= target protein) generated by → TEV protease cleavage (Cat.No. E4310),
Lane 3: Sortase A protein, 1 µg,
Lane 4: Reaction assay, containing a mixture of all proteins shown in lanes 1, 2 and 3, respectively. Incubation for 60 min at 30°C in 1x reaction buffer.
The position of the fusion protein in lane 4 is marked with a red arrow.
Marker: Perfect Color Protein Ladder (Cat.No. E3215).
Note 1: Ligation efficiency is highly dependent on structure and concentration of both substrate and target proteins. Consequently, fusion protein yield is highly assay-dependent and may vary between a few percent and up to 90%.
Note 2: Protein ligase and protease activities, respectively, are two aspects of the same enzyme activity and thus are not cleanly separable. Sortase reactions never proceed with 100 % efficiency, neither with respect to protein ligase, nor to protease activity. Rather an assay specific equilibrium between ligated and cleaved product is obtained. In consequence, sortase assays will always yield a mixture of cleaved and ligated proteins. Thus, further purification steps need to be taken into account, if isolation of fusion proteins is required.

